News, events, publications, jobs and more...
A taste of the future
KFC, the fast-food chain, announced that it is taking a new step towards its “restaurant of the future” by targeting the production of chicken meat by bio-printing. KFC has just signed a cooperation agreement with 3D Bioprinting Solutions, a Russian company that gained recognition in 2018 by testing its technology on board the International Space Station. The partners set themselves the goal of biofabricated chicken "nuggets"the appearance and taste of which will be as close as possible to those of the original product. The first biofabricated "nuggets" will be available this fall.
KFC's press release is available here.
A taste of the future
KFC, the fast-food chain, announced that it is taking a new step towards its “restaurant of the future” by targeting the production of chicken meat by bio-printing. KFC has just signed...
Tissue and Organ Bioengineering doctoral course
Launched at the initiative of IFBF in 2017, the course session "Tissue and organ bioengineering" of the doctoral school "Therapeutic innovation - from the fundamental to the applied" of Paris-Saclay University could not be held in April due to the covid-19 crisis.
It will be held on Monday the 21st, Wenesday the 23rd and Thursday the 24th of September 2020 as a webinar.
Experts from many health, education and research institutions,
- both French (AP-HP, CEA, Ecole Polytechnique, IFBF, Inserm, Institut Pasteur, Institut de la Vision, IRBA, Université Paris-Saclay, UTC),
- and foreign (Health Sciences Institute in Aragon)
as well as from a company (Sanofi),
will present the many specialties contributing to the new discipline of biofabrication:
- cell and organoid culture,
- matrices and "scaffolds",
- bio-printing,
- organs-on-a-chip,
- bio-artificial extracorporeal systems,
- regulatory, economic and ethical aspects.
Please read the detailed program here.
Tissue and Organ Bioengineering doctoral course
Launched at the initiative of IFBF in 2017, the course session "Tissue and organ bioengineering" of the doctoral school "Therapeutic innovation - from the fundamental to the applied" of Paris-Saclay University could not be held in April due to the covid-19 crisis.
It will be held on Monday the 21st, Wenesday the 23rd and Thursday the 24th of September 2020 as a webinar.
Experts from...
Segway founder wants to revolutionize biofabrication
Dean Kamen, the creator of the Segway, founded the Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute, a non-profit organization with approximately 170 members, companies and academic research institutions and endowed with $ 300 million.
His objective is "to collect extraordinary people that have different backgrounds, that probably don’t interact now, but if they did would dramatically accelerate the path to a major breakthrough.” in order to manufacture replacement organs in the next 10 years.
The article from the web publication OneZero is available on its website here or downloadable here.
Segway founder wants to revolutionize biofabrication
Dean Kamen, the creator of the Segway, founded the Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute, a non-profit organization with approximately 170 members, companies and academic research institutions and endowed with $ 300 million.
His objective is...
SARS-CoV-2 and organoids
Organoids are three-dimensional multicellular structures that partially replicate the anatomy of an organ in vitro. They represent an essential field of research in biofabrication. They can be the basic building blocks for making a tissue or bioartificial organ. They are also very useful tools for understanding illnesses and developing their treatments.
This article published in Nature relates the use of lung, but also kidney, liver anc intestine, organoids in the study of COVID-19, especially in the case of its most serious cases. Likewise, these organoids greatly facilitate the initial toxicology tests with a view to developing a treatment.
The article from Nature, freely accessible, can be read on the journal's website here, or downloadable here.
SARS-CoV-2 and organoids
Organoids are three-dimensional multicellular structures that partially replicate the anatomy of an organ in vitro. They represent an essential field of research in biofabrication. They can be the basic building blocks for making a tissue or bioartificial organ. They are also very useful tools for understanding illnesses and developing their treatments.
This article published in Nature...
Researchers produce a model of the early embryonic brain
Research on brain development in the embryo involves many teams. That of the Department of Neuroscience at the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with biotechnology engineers from the University of Lund in Sweden, publishes in Nature Biotechnology an article proposing a model based on a microfluidic system. The use of this technology lays the foundations for the use of 3D tissues for toxicological analysis.
The press release from the University of Copenhagen is available here.
The link to the article is here.
Researchers produce a model of the early embryonic brain
Research on brain development in the embryo involves many teams. That of the Department of Neuroscience at the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with biotechnology engineers from the University of Lund in Sweden, publishes in Nature Biotechnology an article proposing a model based on a microfluidic system.
The production of intestinal organoids
To illustrate our last post dated April 18 about the note of the thematic think tank of the Inserm ethics committee on the ethical issues of the research on organoids, we put online this short video of Nantes University and Inserm showing the production of intestinal organoids (in French).
The production of intestinal organoids
The research on organoids: which ethical issues?
The organoid construction technique is one of the pillars of biofabrication. Organoids are research tools on biological processes and in particular the interaction of cells within an organ.
A thematic think-tank of the Inserm ethics committee examined the ethical issues of research on organoids. Anne Dubart-Kupperschmitt (UMR_S 1193), responsible for two “work-packages” of the iLite project (innovation in Liver tissue engineering - see here) was one of them. Among those interviewed, Jean-Charles Duclos-Vallée (see here), iLite scientific coordinator and chairman of the French Institute of BioFabrication.
We resume below the key points of the note from the working group:
- What characterizes an organoid as such is that it performs certain functions specific to the organ of which it is the organoid
- Organoids organize themselves, spontaneously
- An organoid does not have the same properties and functions as the organ. It is therefore not correct to speak of organoids as mini-organs
- Organoids are research tools that have no application in therapy yet
- It is not always well established that organoids are a good model for the diagnosis and evaluation of therapies
- The current lack, in most cases,of vascularity and / or innervation of these models produced in vitro is a limit which can pose serious problems
- What moral value should be given to living things consideredas a set of parts to be assembled?
- We observe the transitionfrom a natural order to an artificial order, namely theengineering of the living which for some is morally problematic in that it denotes an inappropriate attitude on our part
- Currently, there is no legal standard governing organoids which would make it possible in particular to determine with certainty who is the “owner” or “custodian” of this biological element.
- Science must guarantee a critical approach exercising vigilant control over its own forward-looking advances and committing to promise nothing that cannot be acted upon
Concerning the particular case of brain organoids (cerebroids):
- Characteristics such as sensitivity or awareness are crucial to define the moral status of cerebroids as well as that of any individualbeing
- The meaning given to the terms "emotion" and "consciousness" is essential for understanding the moral status of cerebroids
- If an electrical activity as such cannot be equivalent to consciousness or sensitivity, it cannot be excluded that an entity made up of neurons experiencesmental states since there are correlation and even causal relationshipsbetween mind or spirit and the brain
- Consciousness refers to a "network of consciousness" which is based on the brain's ability to maintain coherent brain dynamics. Thus it is the synchronization and the coherence of the interactions between the areas of the brain, condition not presently present at the level of the cerebroids in vitro, which makes it possible to be aware
- The identification of the means available to tacklethe issueof the moral status of animals in which human cerebroids will be transplanted must be considered in concrete terms
The text of the note from the Inserm ethics committee working group can be downloaded here and is available on HAL (open multidisciplinary archive) here or directly on the Inserm website here.
The research on organoids: which ethical issues?
The organoid construction technique is one of the pillars of biofabrication. Organoids are research tools on biological processes and in particular the interaction of cells within an organ.
A thematic think-tank of the Inserm ethics committee examined the ethical issues of research on organoids. Anne Dubart-Kupperschmitt (UMR_S 1193), responsible for two “work-packages” of the iLite project (innovation in Liver tissue engineering - see here) was one of them. Among those interviewed, Jean-Charles Duclos-Vallée (see here), iLite scientific coordinator and chairman of the French Institute of BioFabrication.
Tissue and Organ Bioengineering doctoral course
Launched at the initiative of IFBF in 2017, the course session "Tissue and organ bioengineering" of the doctoral school "Therapeutic innovation - from the fundamental to the applied" of Paris-Saclay University will be held on April 22, 23 and 24, 2020.
Experts from many health, education and research institutions,
- both French (AP-HP, CCML, CEA, Centrale-Supélec, Ecole Polytechnique, ENS Paris-Saclay, IFBF, Inserm, INSA, Institut Pasteur, Institut de la Vision, IRBA, INTS, Université Paris-Saclay, UTC),
- and foreign (Health Sciences Institute in Aragon, University of Edinburgh, Leuven, Tokyo, Twente),
- as well as companies (Biopredic, Cyprio, GoLiver, Sanofi, Treefrog),
will present the many specialties contributing to the new discipline of biofabrication:
- cell and organoid culture,
- matrices and "scaffolds",
- bio-printing,
- organs-on-a-chip,
- bio-artificial extracorporeal systems,
- preclinical and clinical applications,
- regulatory, economic and ethical aspects.
Please read the detailed program here.
Tissue and Organ Bioengineering doctoral course
Launched at the initiative of IFBF in 2017, the course session "Tissue and organ bioengineering" of the doctoral school "Therapeutic innovation - from the fundamental to the applied" of Paris-Saclay University will be held on April 22, 23 and 24, 2020.
Organ shortage (2)
On the "European Day of Organ Donation and Transplantation" of October 12, 2019, the European Commission published a general assessment for the year 2018.
Over 150,000 patients were waiting for an organ. 6,000 registered patients died.
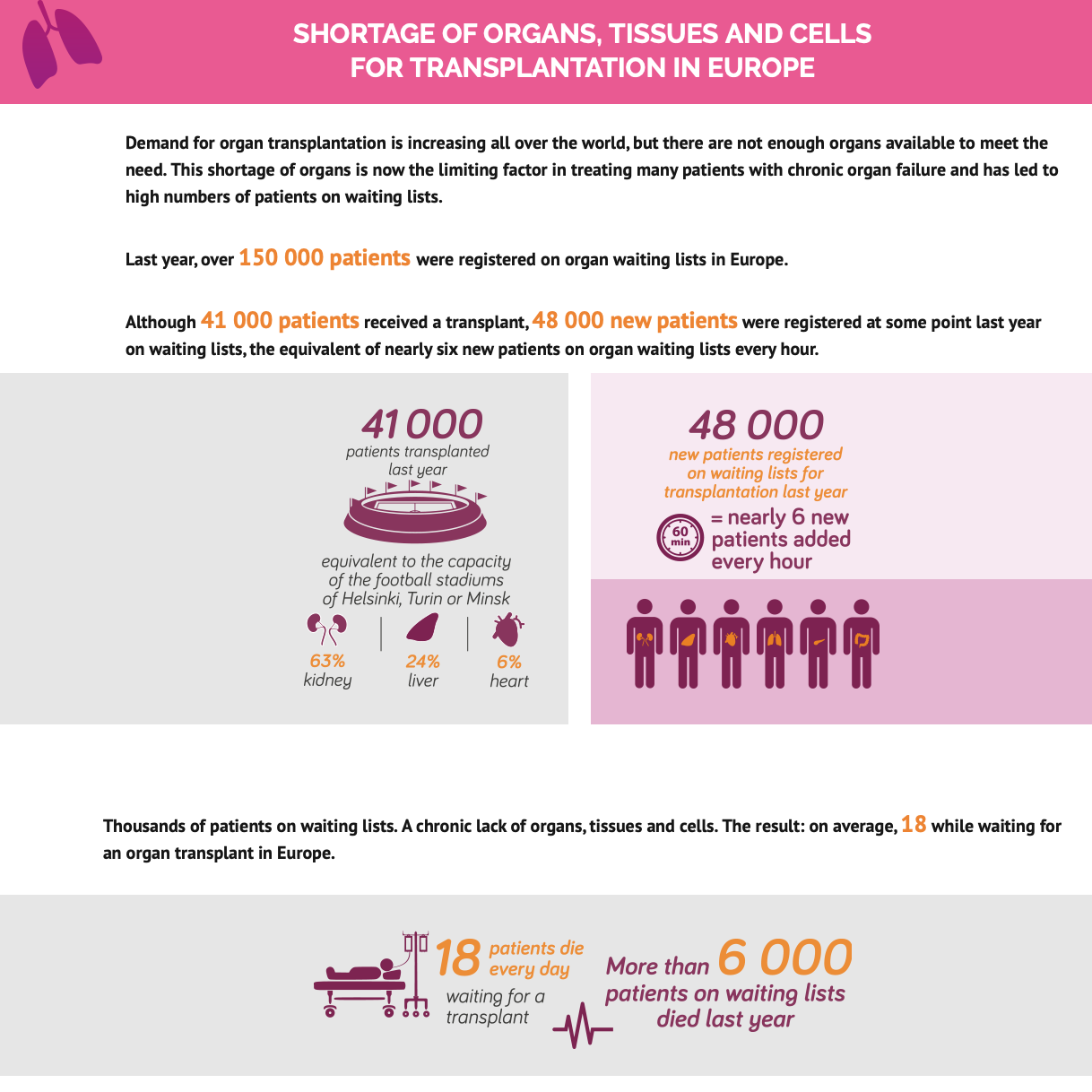
Organ shortage (2)
On the "European Day of Organ Donation and Transplantation" of October 12, 2019, the European Commission published a general assessment for the year 2018.
47th congress of the European Society for Artificial Organs (ESAO)
The 47th congress of the European Society for Artificial Organs (ESAO) will be held at Brunel University in Uxbridge near London from the 8th till the 12th of Septembre 2020.
L’EASO promotes tissue & organ support and regeneration by artificial organ technology.
Candidates for a communication (please read the organisers' welcome letter here) must submit their abstract before the 29th of February.
47th congress of the European Society for Artificial Organs (ESAO)
The 47th congress of the European Society for Artificial Organs (ESAO) will be held at Brunel University in Uxbridge near London from the 8th till the 12th of Septembre 2020.
L’EASO promotes tissue & organ support and regeneration by artificial organ technology.
Organ shortage (1)
We are starting today a series of posts relating to the shortage of organs which does not allow to meet fully, far from it, transplant indications. The number of patients on waiting lists is increasing and is abating. Each year, patients die for lack of a transplant.
An article published in December 2018 in the "Journal of the American Society of Nephrology" draws "the terrible assessment of the kidney shortage" in the United States. The authors estimate that 126,000 patients suffer from end-stage kidney disease each year. Only 16% of them will be able to benefit from a transplant. The other 84% will remain on dialysis with a life expectancy of less than 5 years.
The article in English "The Terrible Toll of the Kidney Shortage" is available here, or directly on the Jasn website.
Organ shortage (1)
We are starting today a series of posts relating to the shortage of organs which does not allow to meet fully, far from it, transplant indications. The number of patients on waiting lists is increasing and is abating. Each year, patients die for lack of a transplant.
An article published in December 2018 in the "Journal of the American Society of Nephrology" draws "the terrible assessment of the kidney shortage" in the United States.
Virtual Physiological Human
By analogy with the expressions in vivo and in vitro, the term in silico was introduced to describe the numerical methods which make it possible to simulate or model a biological phenomenon using computers. The in silico methods are complementary to in vivo and in vitro studies. They provide information that is useful for a good understanding of biological mechanisms.
The robustness of the model strongly depends on the experimental data on which it is based. The development of a model begins with the collection of reliable experimental data. This step is followed by the characterization of the structures with a view to connecting them to the experimental property studied. Data analysis tools are then used to guide the characterization and set up the model itself. Once the model has been developed and in order to estimate its predictive power, additional experimental data is required.
A forthcoming congress in Paris, from August 26 or 28, will bring together specialists in the discipline, in particular researchers who are participating in the iLite research project (see here).
The congress poster can be viewed here.
Save the dates for the VPH2020 Conference organized by Inria and partners in Paris, August 26-28 2020
http://vph-conference.org
Virtual Physiological Human
By analogy with the expressions in vivo and in vitro, the term in silico was introduced to describe the numerical methods which make it possible to simulate or model a biological phenomenon using computers. The in silico methods are complementary to in vivo and in vitro studies. They provide information that is useful for a good understanding of biological mechanisms.
A voice from the past: Nesyamun, scribe and priest of the Karnak temple, addresses us.
British researchers and historians have made a 3-dimensional artificial copy of the vocal tract of Nesyamun, scribe and priest of the temple of Karnak in Thebes (now Luxor) who lived under the reign of Ramses XI (around 1099-1060 BC) .
They scanned his mummy, in excellent condition which hasd been kept in the Leeds City Museum since 1823. By combining the copied organ and an artificial larynx, they allowed Nesyamun to pronounce… a vowel, a sound that no one had heard for 3000 years. Nesyamun's last wishes seem to have been respected: the inscriptions on his sarcophagus indicate that he hoped to be able to address the gods again as he had done during his life.
This example illustrates the results that can be expected in terms of organ functioning by the combination of biological material (mummified in this case) and advanced technologies.
The article, which appeared in the journal Nature, is available here:
Synthesis of a Vocal Sound from the 3,000 year old Mummy, Nesyamun ‘True of Voice’
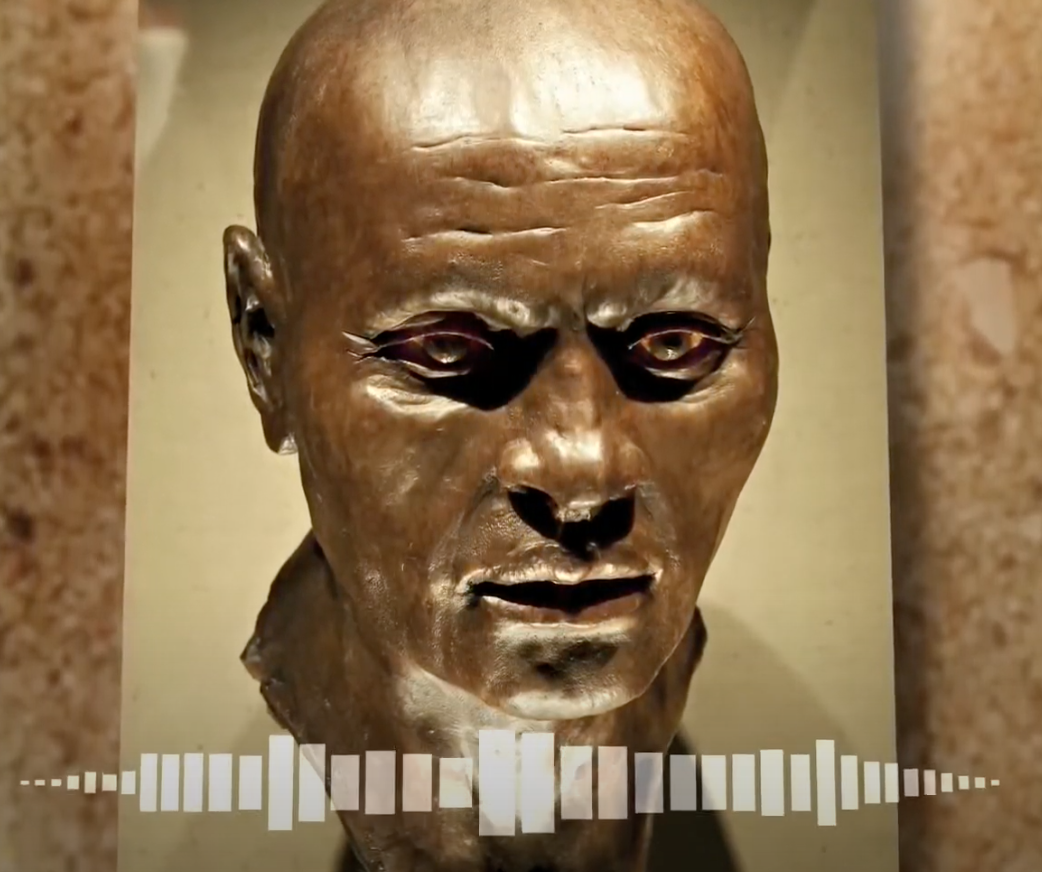

A voice from the past: Nesyamun, scribe and priest of the Karnak temple, addresses us.
British researchers and historians have made a 3-dimensional artificial copy of the vocal tract of Nesyamun, scribe and priest of the temple of Karnak in Thebes (now Luxor) who lived under the reign of Ramses XI (around 1099-1060 BC) .

Poste de Maître de Conférence enseignant à l'ENS Paris-Saclay
Poste de Maître de Conférence enseignant à l'ENS Paris-Saclay
HepaRG self‐assembled spheroids in alginate beads meet the clinical needs for bioartificial liver
HepaRG self‐assembled spheroids in alginate beads meet the clinical needs for bioartificial liver
Unique opportunity for an experienced scientist in stem cell biology to develop a team in the field of liver bioengineering for the construction of liver organoids
Inserm (Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale) is looking to hire an experienced scientist to lead stem cell research, develop a team and take part in projects in the field of liver bioengineering.
The place of work is in fully equipped premises within the Paul-Brousse Hospital campus next to the largest European center for liver transplantation (Centre Hépato-Biliaire) in Villejuif, south of Paris.
Please click below to access to the full proposal.
Unique opportunity for an experienced scientist in stem cell biology to develop a team in the field of liver bioengineering for the construction of liver organoids
Inserm (Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale) is looking to hire an experienced scientist to lead stem cell research, develop a team and take part in projects in the field of liver bioengineering.
Morphogenèse de canaux biliaires dans des supports naturels et artificiels
Morphogenèse de canaux biliaires dans des supports naturels et artificiels
GoLiver Therapeutics a les honneurs de la presse.
GoLiver Therapeutics a les honneurs de la presse.
Inserm & Paris-Saclay UMR-S 1174 offers a post-doctoral position.
UMR-S 1174, a member of the iLite (innovations in Liver tissue engineering) project, aims at producing a functional biliary network which has been a missing element in all previous studies.
Inserm & Paris-Saclay UMR-S 1174 offers a post-doctoral position.
UMR-S 1174, a member of the iLite (innovations in Liver tissue engineering) project, aims at producing a functional biliary network which has been a missing element in all previous studies.
“Tissue & Organ Bioengineering” MOOC: registration is open!
The French Institute of BioFabrication, with Université Paris-Sud and the Hepatinov Academic Hospital Department, releases its “Tissue & Organ Bioengineering” MOOC on the FUN platform. The MOOC is designed for students, scientists and anyone interested in learning about the recent advances and techniques in bioengineering of organs and tissues.
The MOOC flyer is available here:
Présentation-MOOC-Tissue-Organ-Bioengineering.pdf
In order to directly access to the MOOC on the FUN platform, please click here:
https://www.fun-mooc.fr/courses/course-v1:pasteur+96007+session01/about
“Tissue & Organ Bioengineering” MOOC: registration is open!
The French Institute of BioFabrication, with Université Paris-Sud and the Hepatinov Academic Hospital Department, releases its “Tissue & Organ Bioengineering” MOOC on the FUN platform. The MOOC is designed for students, scientists and anyone interested in learning about the recent advances and techniques in bioengineering of organs and tissues.
Click to see more details
Cyprio recruitment
The start-up Cyprio, created in 2017 and specialised in the production of hepatic and pancreatic cell spheroids offers a post-doc position !
Cyprio recruitment
The start-up Cyprio, created in 2017 and specialised in the production of hepatic and pancreatic cell spheroids offers a post-doc position !
Cellenion and Biopredic open a joint laboratory for regenerative liver sciences at Hospital Paul-Brousse, under the French Institute of BioFabrication banner
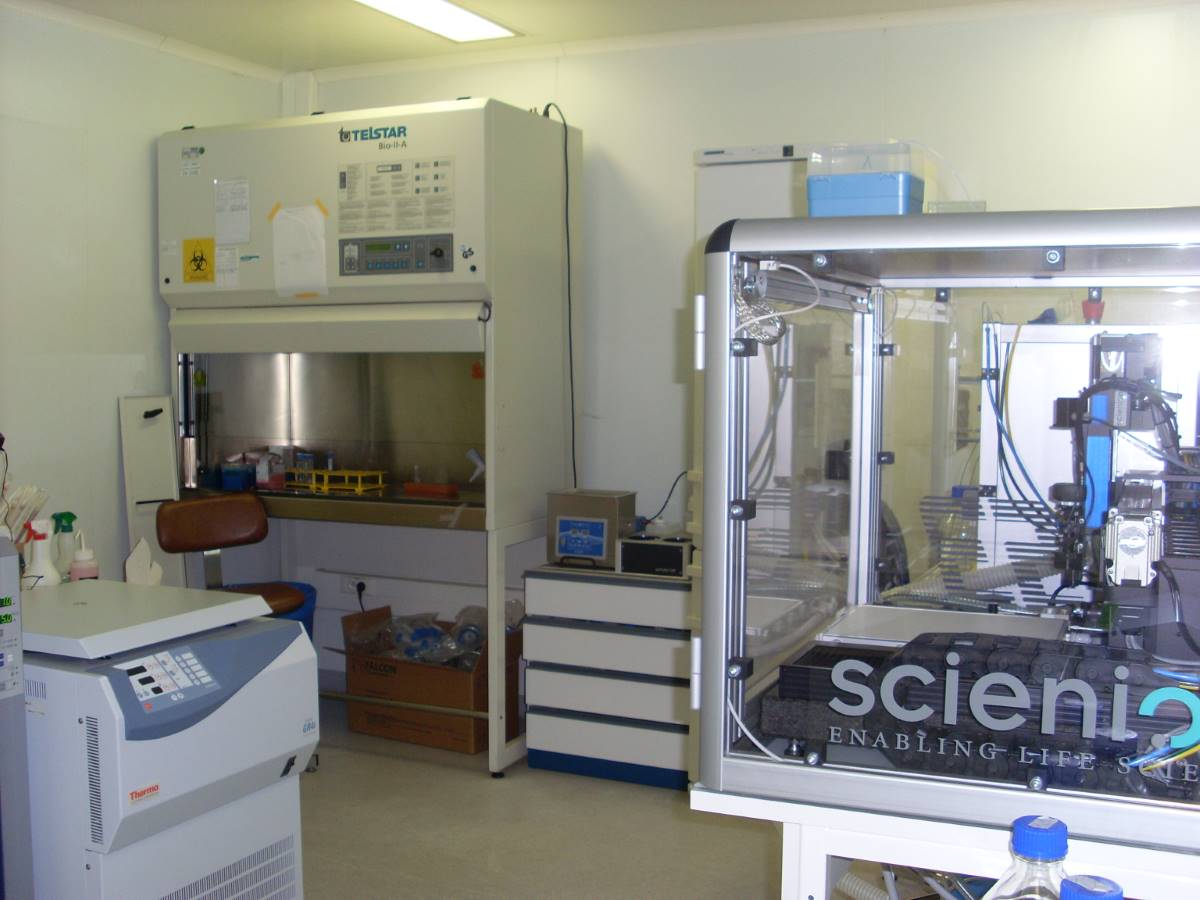
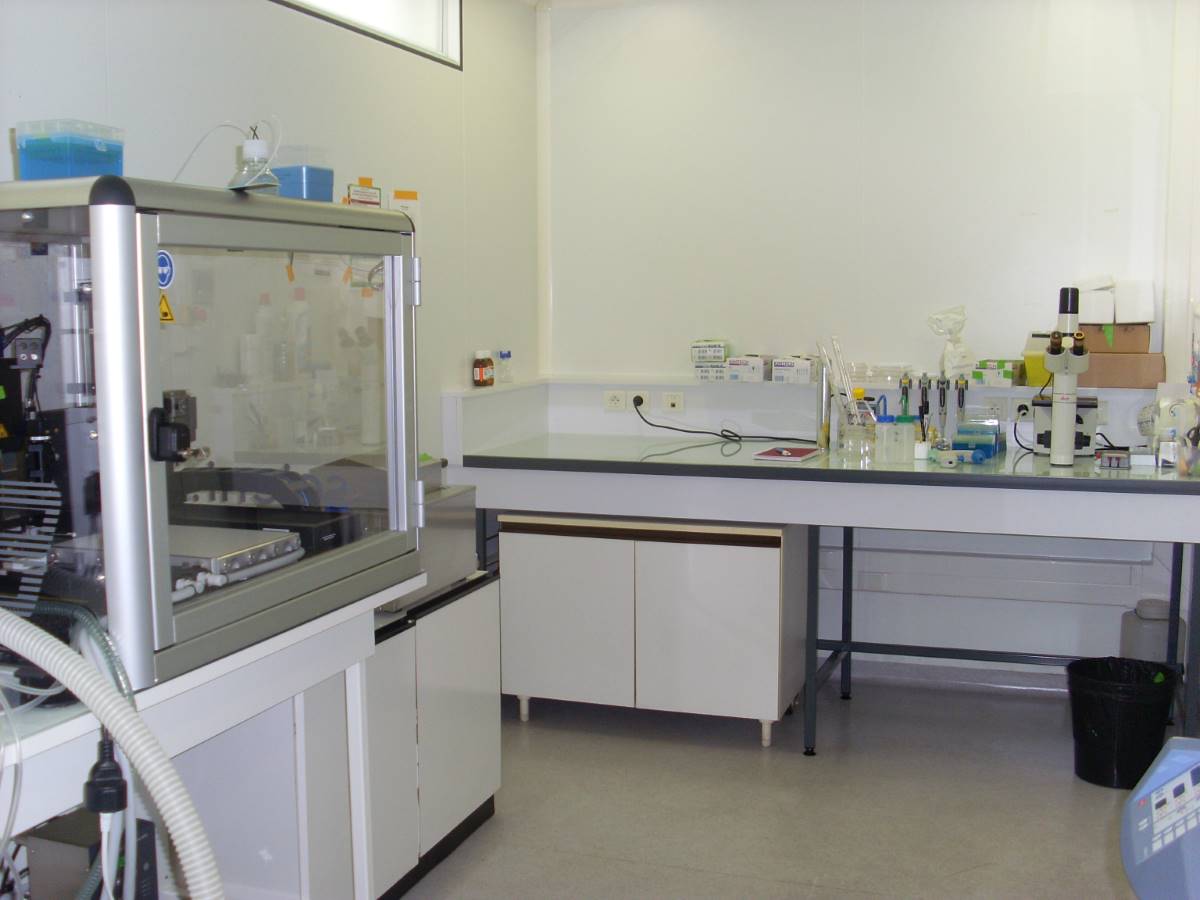


French companies and clinical researchers create a center of gravity for liver bioprinting.
On Wednesday, September 13th, Biopredic International and Cellenion unveiled a new joint “French Institute of BioFabrication” laboratory at Hospital Paul-Brousse in Villejuif (south of Paris).
Cellenion, a daughter company of Berlin based Scienion AG, is a specialist in fully automated printing of viable cells for applications in the fields of bio-printing and bio-analytics. Biopredic International, a company based in Rennes, is a world leader in the production of a large range of cells and associated products for industrial research applications, with focus in pharmacokinetics, toxicology and pharmacology studies.
“Being able to work using bioprinting technologies offering resolution down to single cell is a fundamental tool in biology, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine” said Guilhem Tourniaire, Directeur Général at Cellenion, “With Biopredic, we have found a partner with excellent cell-based products and deep expertise in liver tissues engineering. This new facility will enable close collaborations with world-class clinicians and researchers to drastically accelerate development in liver tissue bioengineering”.
« We are a very customer focused company. As such, we always seek to expand our portfolio of solutions across the latest platform technologies” states Christophe Chesné, Chief Executive Officer at Biopredic and adds “Cellenion’s new acoustic based bioprinting technology is very synergistic with our cell and cell culture capabilities. The expertise of both companies are highly complementary, and working together in a joint laboratory will extend the companies’ clinical reach far beyond what was possible today”.
In recognition to the instrumental role of the association CellSpace in enabling this joint laboratory opening, the laboratory was officially named “CellSpace”. This Paris-based association funded by donations is dedicated to build an international platform devoted to the construction of bioengineered tissues in order to address the shortage of organ suitable for transplantation.
“Cellspace is very pleased that two high tech and key commercial partners for regenerative liver sciences have settled in Villejuif and started joint activities in close proximity to patient care at Paul-Brousse Hospital“ states Prof. Dominique Franco, Founder and Chairman of Cellspace.
Cellenion, Biopredic, CellSpace and scientists at Paul-Brousse Hospital Campus are also members of the iLite (Innovations Liver Tissue Engineering) RHU project. iLite is a 5-year project funded by the National Research Agency (ANR), directed by professor Jean-Charles Duclos-Vallée, that gathers leading French researchers, clinicians and industrial partners to develop an external bio-artificial liver for acute liver failure patients, liver-on-a-chip platform for toxicology studies and, in the longer term, a transplantable bio-constructed liver. The joint laboratories of Cellenion and Biopredic are geared to accelerate research within the iLite consortium and establish new collaborations with researchers and clinicians at Paul-Brousse Hospital as well as other university hospitals in the region.
Cellenion and Biopredic open a joint laboratory for regenerative liver sciences at Hospital Paul-Brousse, under the French Institute of BioFabrication banner
French companies and clinical researchers create a center of gravity for liver bioprinting.
On Wednesday, September 13th, Biopredic International and Cellenion unveiled a new joint “French Institute of BioFabrication” laboratory at Hospital Paul-Brousse in Villejuif (south of Paris).
External bio-artificial liver: Cécile Legallais’s interview
Cécile Legallais, a CNRS/Université de Technologie Compiègne (UTC) researcher, comments on her project of an external bio-artificial liver. UTC is a member of CellSpace and Mrs Legallais ‘s team participates in the iLite project (see below).
Listen to the interview on CNRS/la radio (in French, 0-11mn, 35-38mn)
External bio-artificial liver: Cécile Legallais’s interview
iLite recruitment
The Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA) is one of the members of the iLiTE project (innovation in Liver Tissue Engineering) and recruits a post-doctoral research scientist in the fields of micropatterning and bioprinting.
iLite recruitment
The Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA) is one of the members of the iLiTE project (innovation in Liver Tissue Engineering) and recruits a post-doctoral research scientist in the fields of micropatterning and bioprinting.